An Overview of the Pros, Cons, and Benefits of Driving an Electric Vehicle
Put together by the team at Lemonade
If you’ve gotten sticker shock after filling up your car lately, you’re not alone.
Paying for gas is one of the inevitable but frustrating aspects of driving a car. But you’ll be happy to learn that’s not the only option.
Electric vehicles can rescue you from gas prices all while helping to improve the environment.
For more info on how electric cars work and their many benefits, keep reading.
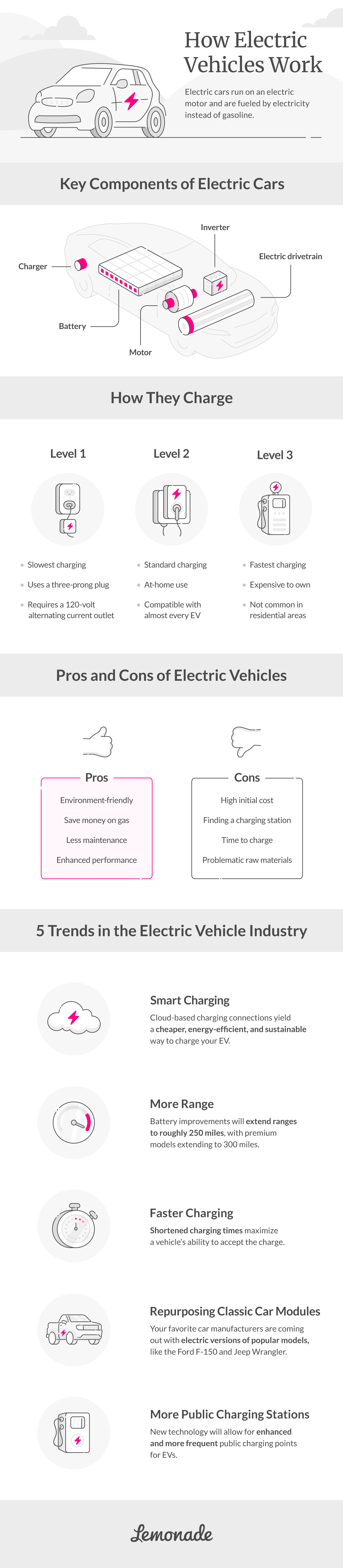
Benefits of Driving an Electric Vehicle
There are many benefits of driving a green vehicle. We break down a few of the top benefits below:
Federal, state, and local incentives:
- Federal tax credits are available for those buying an EV. Those credits range from $2,500-$7,500 depending on the car company and model, year, and your location. And if you lease your vehicle, dealerships often factor in the tax credit to your lease which can result in a lower down payment or lower monthly payments.
- The Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP) provides rebates directly to EV owners or lessees.
- Local air districts and electric utilities also offer incentives and rebates for the purchase or lease of an EV and for installing a home charging station. You can search your zip code to find local rebates here. For those in Georgia seeking to make the transition to electric vehicles more accessible and affordable, visiting a pre-owned car lot like EchoPark in Atlanta can offer competitive options alongside traditional inventory.
Gain access to HOV lanes:
- In California, EV drivers are able to gain access into the carpool (or HOV) lanes even if they’re driving solo. This is due to the Clean Air Vehicle (CAV) program.
Better health for you and your neighbors:
- Studies have found that electric cars’ effect on air quality could lead to lower health care costs.
- Gas-powered vehicles create pollutants found in car exhaust that cause health complications like asthma and bronchitis. By switching to an EV, you’re lessening your own exposure to these pollutants and the exposure of your loved ones.
Pros and Cons of Electric Vehicles
While electric vehicles boast a long list of benefits, both for the environment and your wallet, they’re not for everyone. Read up on the pros and cons of EVs below.
Pros:
- Good for the environment: Electric vehicles boast zero emissions, which reduces smog and greenhouse gases. This translates to cleaner air and overall better health for our planet.
- Less money spent on gas: You’ll also save a good chunk of change by not having to shell out at the gas pump. EV owners can expect to pay up to half the price for power charging than they would to fuel a gas-powered car.
- Less maintenance: Electric vehicles have far fewer parts than your average car and you won’t have to worry about an oil change or changing out fuel filters.
- High performance: EVs have quick acceleration and unmatched performance, and some EV drivers say that they’re more fun to drive than traditional cars.
Cons:
- High initial cost: Electric cars cost less to operate and maintain, but the trade-off is the high purchase price. That being said, you might be eligible for a federal tax credit to help offset the cost. However, credit amounts can vary by location, car company, model, and year.
- Finding charging stations: Charging stations aren’t as common as gas stations. If you plan on driving long distances, an EV may not be right for you because you may have trouble finding charging stations along the way.
- Time to charge: Filling up your car with gas can take two to three minutes, but charging your EV can take hours. The time will vary depending on the model of your car.
Types of EVs
There are four main types of electric cars: battery electric vehicle (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), and hydrogen electric vehicles (fuel cell).
We dig into what each of these types mean below.
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) is a fully electric car powered exclusively by electricity. They have an electric car motor that draws current from the electric battery without the use of a conventional internal combustion engine.
BEVs also have fewer components than a plug-in hybrid, so they tend to boast lower maintenance costs because they don’t require fluid changes or tuneups.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
A PHEV combines an electric car motor and battery with a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE).
PHEVs offer the ability to switch the ICE off and run entirely on electric mode. PHEV owners can choose to top off their car with fuel or electricity.
A PHEV can operate on gasoline alone if the electric battery isn’t charged, or they can use the battery charge if they run out of fuel. This makes them a great option if you plan on using an EV for longer distances or road trips.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) uses a combination of fuel and electricity to run. This is great for people who aren’t ready to fully commit to electric cars, but want to reap some of their benefits.
HEV owners often use the electric features for stopping and accelerating and prefer to use the internal combustion engine when cruising down the freeway.
When conditions are suitable, the electric motor will automatically activate and recharge through regenerative braking.
Hydrogen Electric Vehicles (Fuel Cell)
Hydrogen electric vehicles (fuel cell) are similar to battery electric vehicles (BEV) in the sense that they only use electricity for power.
The fuel cell electric vehicles create their own energy through a chemical reaction with the use of hydrogen. These cars can be filled with hydrogen and do not require a standard charging system for electricity.

Photo by Jenny Ueberberg on Unsplash
Electric vehicles are an exciting development that you’ll likely see more of in the coming years.
For even more details on electric vehicles, including how they work and the biggest trends in the industry, our friends at Lemonade have created this helpful infographic.